- Vet to the Future
- Posts
- 📀 Electric Healing, Social Vaccines, and Virtual Companions
📀 Electric Healing, Social Vaccines, and Virtual Companions
Spinal cords reboot through electric fields, bats vaccinate each other with gel, and therapy dogs reduce stress—virtually.

Issue #15 | Tuesday, July 8, 2025 | ⏳ Read Time: ~6 Minutes | 1,211 Words
👋 Welcome to Vet to the Future
This week, we’re exploring what happens when biology, behavior, and technology become the delivery systems for healing. From electric-field implants that reboot spinal cords to bats distributing vaccines through grooming and virtual therapy dogs reducing stress with just five minutes of screen time, this issue follows a powerful shift: science that listens—to instinct, data, and emotion.
If you’ve ever wondered how an algorithm, a spinal cord, and a golden retriever might all become healthcare tools—you’re in the right place.
⚡ Quick Hits: Your Fast Facts Roundup
🐕 Virtual Therapy Dog Reduces Stress
Five-minute videos of therapy dogs significantly reduce anxiety in hospitalized and stressed individuals. 🔗 Read More
🧠 AI Maps H5N1 Immune Evasion
New tool reveals how bird flu mutations weaken antibody binding. 🔗 Read More
🦷 Dogs’ Chewing Captured with Motion Sensors
Tracking canine jaw mechanics reveals pure hinge motion and chewing-frequency shifts. 🔗 Read More
🧬 Paralyzed Rats Regain Function via Electric ImplantsLow-frequency electrical stimulation helps spinal cords regenerate axons. 🔗 Read More
🦇 Vampire Bats Spread Rabies Vaccine via Grooming
Researchers developed a topical rabies vaccine that spreads through vampire bats’ natural grooming behavior—immunizing colonies without injections. 🔗 Read More
🧪 Exercise-Mimicking Molecule Identified
New compound activates key metabolic and anti-aging genes. 🔗 Read More
🌡️ Infrared Thermography Shows Promise in Tumor Detection
A study using heat imaging found distinct temperature patterns in canine skin tumors. 🔗 Read More
🧠 Can AI Nanobots Detect Disease?
Tech futurists explore readiness and risks of diagnostic nanotechnology. 🔗 Read More
📊 Maze Tests Unlock Animal Memory
Flexible memory assays help study cognition in nonhuman species. 🔗 Read More
📈 Decoding DNA for Cancer Risk
AI-enhanced sequencing sharpens precision oncology predictions. 🔗 Read More
🧏♂️ Camel Milk Shows Anti-Asthma Properties
Unique compounds may reduce inflammation and airway constriction. 🔗 Read More
🌬️ Breathalyzers Enter Medicine
The fields of breathomics and exhalomics are advancing non-invasive diagnostics by analyzing chemical markers in exhaled air. 🔗 Read More
🤿 Deep Dives: Big Stories, Bigger Impact
AI Reveals H5N1’s Growing Immune Evasion
📝 Emily Ready | June 20, 2025 | ASM Press | 🔗 Read More
The Scoop: Researchers at UNC Charlotte used AI and physics-based models to analyze thousands of H5N1 hemagglutinin protein sequences. They found that recent viral mutations increasingly weaken binding to human antibodies, signaling a mounting ability to evade immunity—and confirming the virus’s drift toward immune escape.
Given over 70 human infections and one U.S. death to date, these findings are critical. AI-driven insights into evolving immune evasion can guide surveillance priorities and antibody therapy development—alerting veterinarians and health authorities to emerging zoonotic threats.
🧠 Why it matters:
✅ Zoonotic risk forecasting – Helps predict potential cross-species transmission. ✅ Targeted antibody response – Improves understanding of immune escape mutations.
✅ One Health relevance – Aligns human and veterinary disease monitoring.
Join the Conversation: What other pathogens could benefit from real-time immune surveillance like this?
Virtual Therapy Dogs Reduce Stress via Video
📝 Paul McClure | July 01, 2025 | New Atlas | 🔗 Read More

The Scoop:
In a study by UBC-Okanagan and Brock University, nearly 1,100 participants (students and adults) watched five-minute videos of therapy dogs. Stress assessments using a visual analog scale dropped significantly after exposure—an accessible, low-cost intervention that mirrors benefits of live animal therapy without requiring in-person visits.
This virtual therapy model, part of the BARK program, was motivated by accessibility needs heightened during the COVID-19 pandemic. It shows that passive engagement—even without interactive behavior—can deliver emotional relief, offering hospitals and care settings a scalable option for mental wellbeing.
🧠 Why it matters:
✅ Scalable therapy – Brings animal-assisted stress relief to more people.
✅ Low-cost intervention – Easy to implement with video access.
✅ Validates passive animal media – Shows real effect without physical contact.
Join the Conversation: Should virtual therapy animals be added to standard hospital wellness tools?
Hinge-Only Jaw Motion in Dogs Observed
📝 Stephanie Goldschmidt et al | July 02, 2025 | Frontiers in Veterinary Science | 🔗 Read More
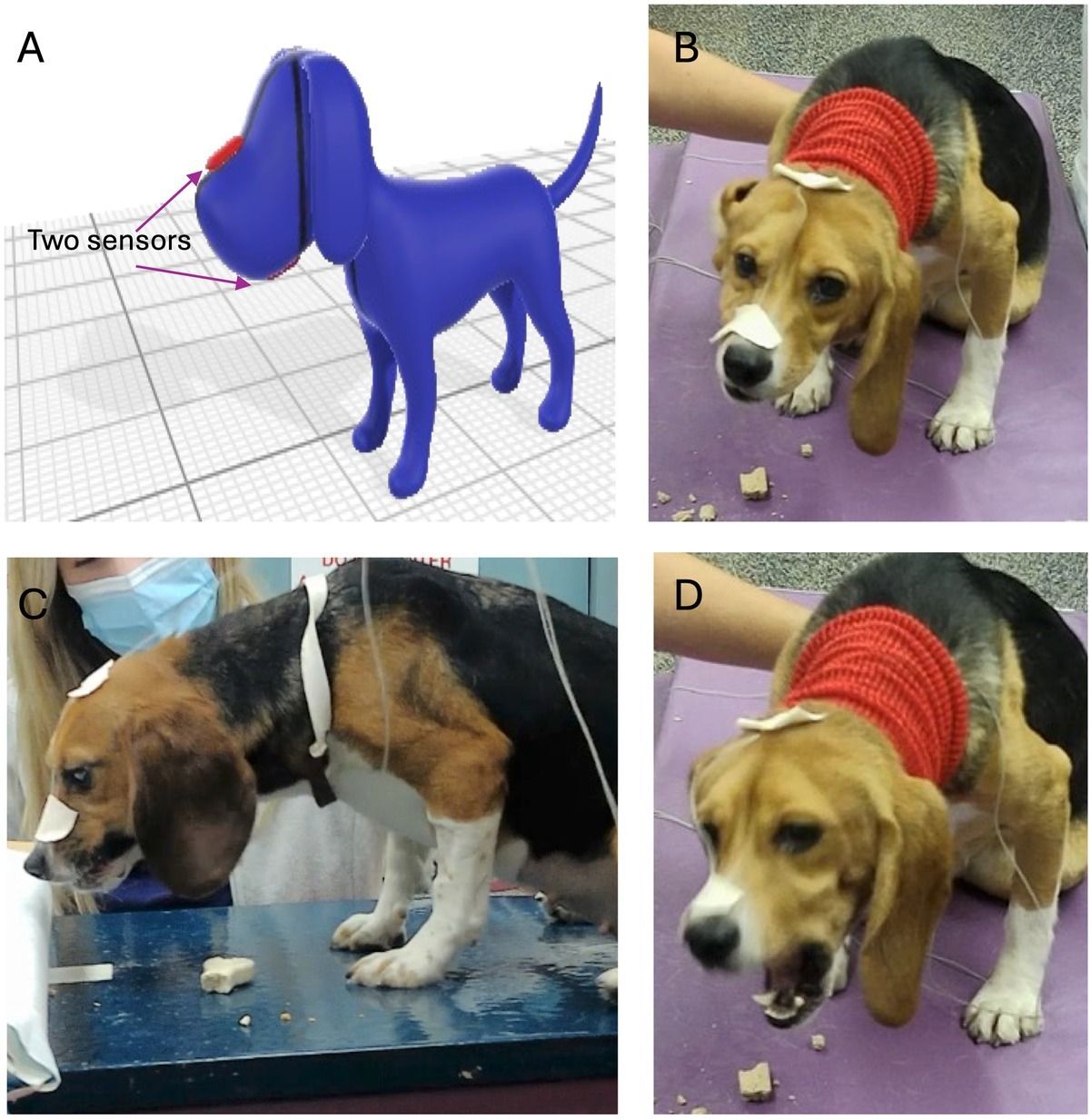
The Scoop:
A study using optical and electromagnetic motion tracking observed beagles chewing various foods. Results confirmed that their jaw motion is a pure vertical hinge without clinically meaningful lateral movement. Chewing frequency, however, correlated with food toughness—kibbles triggered higher chewing rates than softer foods.
This clarified characterization fills a gap in canine dental biomechanics. These insights can fine-tune ex-vivo models of chewing, guide rehabilitation after oral injury, and inform design of veterinary dental tools tailored by diet or breed.
🧠 Why it matters:
✅ Dental treatment planning – Supports accurate diagnosis and prosthetic fitting. ✅ Breed-based studies – May reveal differences across skull types.
✅ Clinical rehab modeling – Informs bite-force recovery protocols.
Join the Conversation: What foods or chews do you recommend post-jaw injury or surgery?
Electric-Field Implant Restores Rat Mobility
📝 Abhimanyu Ghoshal | July 06, 2025 | New Atlas | 🔗 Read More
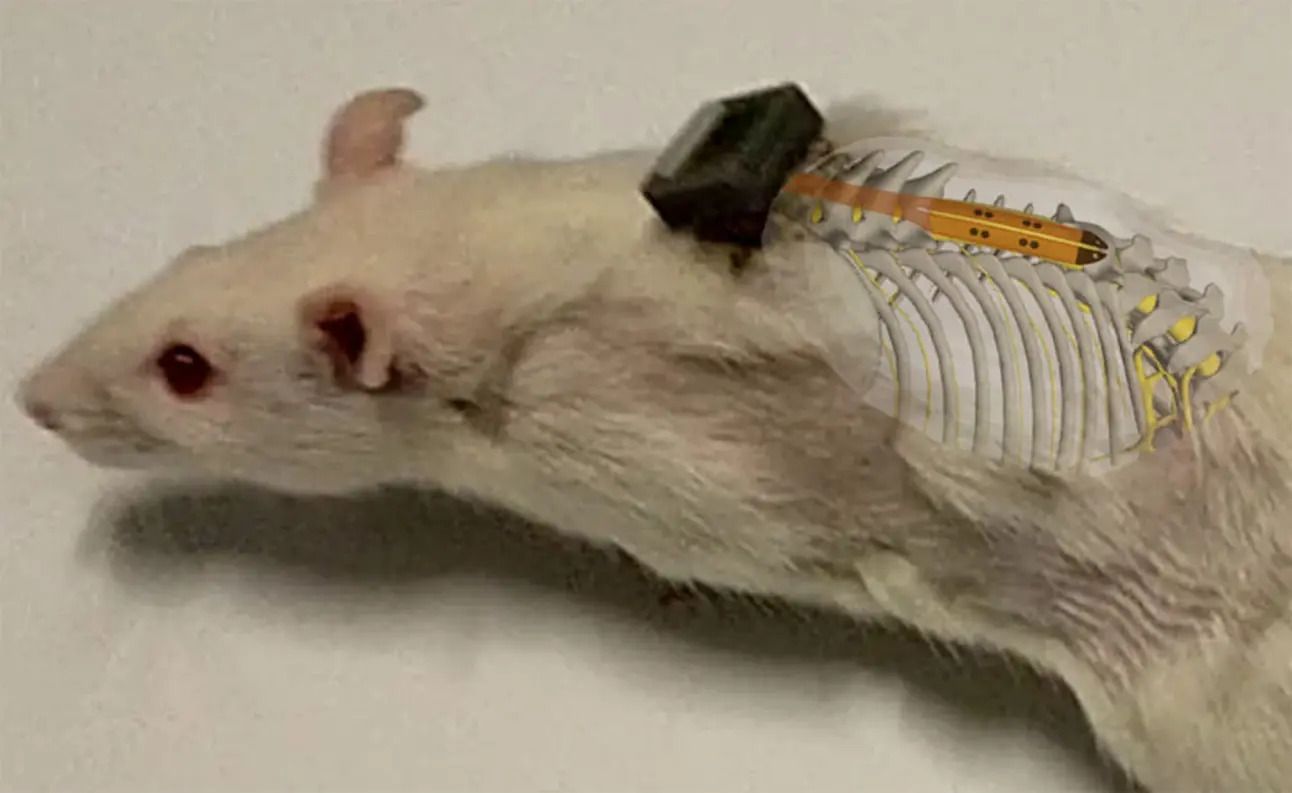
A visualization of the spinal cord implant embedded subdurally in a rat. Image courtesy of the researchers
The Scoop:
A joint team from the University of Auckland and Chalmers University implanted ultra-thin electric-field devices on spinal cord injury sites in rats. Daily low-frequency electrical stimulation over 7–12 weeks led to regrowth of nerve fibers and significant improvements in hind-limb use and touch sensation—without inflammation or tissue damage.
This represents a minimally invasive therapeutic leap: direct electric field treatment encouraging regeneration. While rats naturally recover more than humans, this proof-of-concept could pave the way for veterinary and human neuro-rehabilitation devices.
🧠 Why it matters:
✅ Nerve regrowth support – Enables partial restoration after injury.
✅ Minimally invasive approach – Less risky than mechanical implants.
✅ Vet + human medicine crossover – Expands spinal therapy options.
Join the Conversation: Could electrical stimulation one day become standard rehab for injured pets?
🙌🏼 Impressive Animals 🐾
Bats Spread Rabies Vaccine Through Grooming
📝 Science | July 2025 🔗 Read More

The Scoop:
Scientists have developed an innovative rabies vaccine strategy that uses vampire bats’ natural social grooming behavior to distribute oral vaccines. By applying the vaccine gel to a small number of bats, researchers observed how it spread through grooming to protect entire colonies. This method offers a game-changing, non-invasive solution for managing rabies outbreaks in wild populations.
This approach could be especially valuable in Latin America, where vampire bats are major reservoirs for rabies. The study shows how behavioral ecology can become a delivery mechanism for public health—and opens the door for broader social-spread vaccination strategies.
🧠 Why it matters:
✅ Behavior-based immunization – Uses grooming instead of injections.
✅ Zoonotic disease control – Tackles rabies at the colony level.
✅ Ecological strategy – Protects wildlife without disrupting it.
Join the Conversation:
Could this method apply to other socially bonded species?
💊℞: Dose of Humor
📣 Support Vet to the Future!
Love this newsletter? Buy me a coffee and support my work! ☕ ko-fi.com/rossimiano
📢 Want to sponsor Vet to the Future? Let’s talk!
You're still here? Awesome. Since you're clearly a newsletter connoisseur, here's another one I think you'll appreciate.
|
🎬 Closing Thoughts
What do therapy dogs on screens, self-vaccinating bats, and electric-field spinal implants have in common? They’re all part of a growing toolkit that blurs the line between instinct and innovation. Whether we’re restoring movement through circuits or relieving stress with a wagging tail on video, the future of care is becoming more intuitive, less invasive, and deeply connected.
Here’s to a future where healing feels natural—even when powered by tech.
Cheers,
— Ross
📩 Want to submit a story? Let’s connect → [email protected]!




Reply